Navigating IPC Standards in PCB Design and Manufacturing
- TapRen Team

- Aug 6, 2025
- 8 min read
Updated: Aug 20, 2025

Abstract
This summarizes IPC standards, the global standards for PCB assembling, producing, and designing. The article explains how such standards ensure PCB production is more reliable, qualitative, and uniform. The article refers to general categories, including design, performance, material specifications, assembly, and testing, and how these factors work together to achieve higher cost benefits, improved performance, and world-level compliance. The article provides hands-on guidance on incorporating, maintaining, and implementing IPC standards in design and production processes to achieve higher product quality and industry acceptance.
Introduction
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the pillars of electronics today, providing effective electrical contacts in most equipment. To guarantee consistency, quality, and reliability, the electronics industry adheres to IPC standards, a series of guidelines widely adopted by the Institute for Printed Circuits (IPC).
For assemblers, designers, and PCB manufacturers, knowledge and implementation of these standards are key to producing high-quality, compliant industry boards. This book covers the different IPC standards, their categorization, and the best approach to approach them to enhance efficiency and achieve best practices in PCB design and manufacturing.
Understanding IPC Standards
What are IPC Standards?

IPC standards are global standards that provide best practices in PCB manufacturing, design, assembly, and testing. Developed by the Institute for Printed Circuits (IPC), they give the electronics industry interoperability, quality, reliability, and consistency.
Through its stringent material, fabrication, and inspection requirements, IPC standards minimize costs, eliminate defects, and enhance product performance. IPC standards simplify international compliance by coordinating PCB manufacturing with industry and customer requirements and regulations. Whether it is a simple PCB or a complicated multilayer board, IPC standard compliance guarantees quality and industry-regulated manufacturing.
Why is the IPC Standard Essential?

IPC standards are crucial for ensuring an industry standard for PCBs in terms of quality, reliability, and performance. When followed by manufacturers, these international standards enable the maximum production rate, minimize fault rates, and prolong product life cycles. This is why following IPC standards is important:
Improved Quality
IPC standards impose stringent design, material, and manufacturing requirements on high-reliability PCBs, aiming for very low defect rates. By following such standards, manufacturers can minimize issues such as poor solder joints, delamination, and electrical failures. IPC-A-600 and IPC-A-610 conforming quality inspections can identify likely defects in the early phases of production, thereby ensuring that defective products never reach the market. This ultimately leads to increased customer satisfaction and long-term reliability.
Cost Efficiency
IPC requirements eliminate errors and rework, resulting in significant cost savings. By using recommended design rules (IPC-2221) and material specifications (IPC-4101), assemblers can prevent wasteful overage due to faulty fabrication or assembly. Inspecting and testing in a standardized fashion also enables defects to be trapped early on rather than leading to the expense of recall or failure. In the long term, compliance with IPC boosts the manufacturer's total efficiency and profitability.
Global Compliance
IPC standards are universally accepted in the electronics sector and are hence required to meet international manufacturing standards. The majority of OEMs, suppliers, and regulatory bodies require adherence to the IPC standard to ensure consistency in production. With such standards, firms can seamlessly work with global partners and meet export regulations. Standardization also facilitates quality audits and certification, which in turn boosts a company's reputation in the market.
Better Performance
High-quality PCBs are essential to ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of electronic devices. IPC standards provide performance criteria, material tolerances, and assembly criteria that prevent premature failure. By conforming to IPC-6012 for rigid PCBs or IPC-6013 for flexible PCBs, manufacturers can be sure their boards meet mechanical, thermal, and electrical specifications. The result is more robust, reliable products for aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
By integrating IPC standards into design, manufacturing, and testing, businesses can satisfy industry demands by creating high-quality, low-cost, and globally compliant PCBs.
Categories of IPC Standards and How to Navigate Them
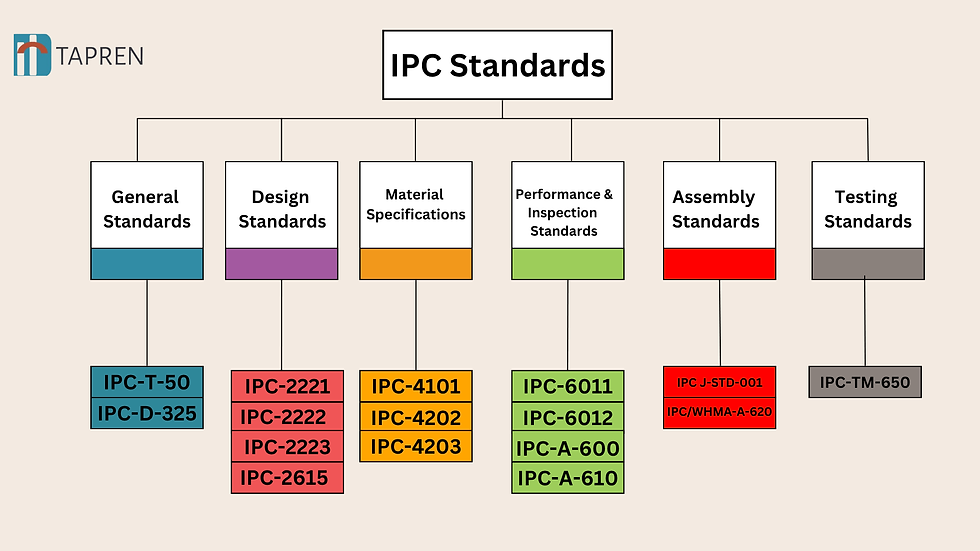
General Standards
These are the standard documents that provide industry terminology and documentation standards for PCBs so that there is uniformity in communication and manufacturing.
IPC-T-50: Standard Terms and Definitions for PCB Industry
IPC-T-50 is a very detailed glossary that the electronics industry uses to offer standard terms for delineating PCB design, manufacturing, and assembly. Standard terms help designers, manufacturers, and assemblers communicate more easily by eliminating misunderstandings between parties. Consistency also applies in global supply chains, preventing mistakes brought about by misinterpretation. Whether you are designing PCB layouts or establishing quality control definitions, using IPC-T-50 ensures technical reports are delivered with accuracy and clarity.
IPC-D-325: Manufacturing Documentation Requirements for PCBs
IPC-D-325 specifies drawings, data forms, and documentation requirements for assembly and PCB manufacturing. The standard provides assurance that manufacturers are supplied with the right, correct, detailed, and standard information required to produce correctly. The data comprises fabrication drawings, schematics, bill of materials (BOM), and Gerber files. Compliance with this standard minimizes miscommunication, reduces errors in PCB production, and enhances collaboration among designers, manufacturers, and assembly teams.
How to Use
Start by learning about IPC-T-50 so that the correct terminology is employed in design documentation. When documenting PCB preparation, adhere to IPC-D-325 so that instructions to manufacture are clear, comprehensive, and consistent.
Design Standards
These requirements necessitate adherence to specific PCB design and layout regulations to ensure functionality, reliability, and manufacturability.
IPC-2221: General Standard for PCB Design
IPC-2221 is the general standard for PCB design. It discusses the general design guidelines, materials, and design performance requirements. IPC-2221 provides guidelines for conductor spacing, dielectric material, and thermal considerations. It can be applied to every form of PCB and ensures consistency in design for various fabrication methods. IPC-2221 compliance ensures that the designers obtain manufacturable, cost-effective, and reliable PCB designs.
IPC-2222: Design Standard for Rigid PCBs
IPC-2222 is a sectional standard in IPC-2221 but targets rigid PCBs. It puts requirements on layer stack-up, via structure, hole sizes, and component attachment for manufacturability. The application of IPC-2222 helps designers keep trace routing, EM Interference (EMI), and maintain mechanical stability within rigid PCBs. This standard plays a vital role in obtaining high-yield manufacturing and long-term reliability for rigid boards.
IPC-2223: Flexible PCB Design Standard
IPC-2223 provides guidelines for flexible circuit design, including bend radius, material selection, and stress management. In contrast to rigid boards, flex PCBs require special mechanical robustness and flexibility. Due to bending, IPC-2223 prevents designers from cracking, delamination, and signal loss. Manufacturers' compliance with IPC-2223 enables the provision of flex circuits with reliability and performance specifications in various applications, including medical applications and automotive electronics.
IPC-2615: PCB Size and Tolerances
IPC-2615 is a standard industry document that establishes mechanical requirements and dimensional tolerances for PCB manufacturing. It includes trace width specifications, solder mask clearances, hole sizes, and board thickness tolerances. Compliance with IPC-2615 provides correct manufacturing, eliminates misalignment errors, and offers consistency between fabrication lots. The standard is crucial for achieving close tolerances in high-density PCB designs.
How to Use
Specify the PCB type rigid, flex, or hybrid, and cite the correct standard (IPC-2221, IPC-2222, IPC-2223). Use IPC-2615 to define tolerances to allow for correct fabrication and assembly.
Material Specifications
These cover standards that outline the material specifications and properties for PCB fabrication for performance and quality control.
IPC-4101: Base Materials for Rigid and Multilayer PCBs
IPC-4101 outlines the electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties of laminate and prepreg materials for use in multilayer and rigid printed board circuits. Materials are classified by type based on parameters such as glass transition temperature, flame retardance, and dielectric constant. IPC-4101 will enable PCBs to withstand environmental, mechanical, and electrical stress. Selecting the correct IPC-4101-type material will optimize board performance and extend its lifespan.
IPC-4202: Flexible Base Dielectric Materials
IPC-4202 defines the material properties of flexible dielectric substrates for flex circuits. It offers recommendations for polyimide films, polyester, and other flexible dielectrics that must be able to withstand repeated bending and thermal cycling. This standard ensures that flex PCBs are electrically and mechanically stable in applications like wearables, aerospace, and medical devices.
IPC-4203: Adhesive Coated Dielectrics for Flex Circuits
IPC-4203 standardizes adhesive-coated dielectric films for manufacturing flexible PCBs. IPC-4203 calls out bond strength, thermal resistance, and moisture absorption to ensure reliable flex circuit performance. Adherence to IPC-4203 avoids delamination, cracking, and failure of adhesives in flexible PCBs.
Instructions:
In rigid PCBs, employ a material complying with IPC-4101. In flex circuits, employ base materials to IPC-4202 and adhesives to IPC-4203 to meet long life and electrical reliability.
Performance and Inspection Standards
These standards establish PCB quality, reliability, and acceptance requirements regarding inspection and test specifications.
IPC-6011: Generic Performance Specification for PCBs
IPC-6011 provides generic performance requirements for flex, metal-core, and rigid boards. It includes requirements for environmental resistance, mechanical properties, and electrical performance. The manufacturer uses this standard to verify the PCB's reliability before proceeding to mass production.
IPC-6012: Performance Specification for Rigid PCBs
IPC-6012 is a standard that builds upon IPC-6011, addressing rigid boards specifically. It classifies PCBs into different performance classes (Class 1, 2, and 3) based on application criticality. This standard helps manufacturers ensure that rigid PCBs are suitable for certain durability and functionality requirements.
IPC-A-600: Acceptability of Printed Boards
IPC-A-600 is a visual standard for acceptance to defines acceptable and nonconforming PCB defects. It features high-magnification images to examine solder mask defects, pad damage, plating issues, and other defects. It is a crucial standard for manufacturing quality inspections of PCBs.
IPC-A-610: Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies
IPC-A-610 provides specifications for soldering, component placement, and assembly quality inspection. It is widely applied in PCB assembly processes to determine whether a finished product meets industry workmanship requirements.
Usage:
Comply with IPC-6011 and IPC-6012 for performance checks. Use IPC-A-600 and IPC-A-610 for inspection and classifying PCB defects.
Assembly Standards
These standards guide PCB assembly, soldering practices, and wire harness specs.
IPC J-STD-001: Requirements for Soldering Electronic Assemblies
IPC J-STD-001 requires acceptable soldering materials, processes, and quality control procedures. It guarantees high-reliability solder joints for consumer, industrial, and military electronics.
IPC/WHMA-A-620: Wire Harness and Cable Assembly Standard
IPC/WHMA-A-620 specifies the quality requirements for cable and wire harness assemblies. It covers crimping, soldering, insulation, and strain relief to ensure long-term reliability.
Testing Standards
IPC-TM-650: Test Methods Manual
IPC-TM-650 is a collection of standardized test procedures for establishing the electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties of PCBs. It ensures that PCBs meet performance and reliability specifications.
How to Use:
Before deployment, IPC-TM-650 will be utilized to conduct functional, thermal, and mechanical tests on PCBs.
Best Practices Using IPC Standards

Choose the Suitable Standard
Identify which category applies to your process—design, materials, assembly, or inspection—and apply the corresponding IPC standard. In fact, IPC-2221 covers general design practices, while IPC-6012 ensures the quality of PCB fabrication. Applying the correct standard gives compliance and effectiveness.
Stay Updated
IPC standards are regularly revised to incorporate new technologies and industry requirements. Always use the latest versions to provide quality, reliability, and regulatory compliance. Staying current prevents outdated methods from disrupting production.
Become IPC Certified
IPC certification offers professional credibility and ensures conformity to industry best practices. Training courses like IPC-A-610 for assembly and IPC-6012 for fabrication help professionals become proficient in inspection and quality control.
Embed Standards in CAD & Production
Several ECAD software (Altium, KiCad, Eagle) support IPC-standard design rules to ensure manufacturability. Manufacturers implement IPC-6012 for fabrication, and IPC-A-600 is used for defect classification, improving quality checks, and reducing faults.
Conclusions
It's required that PCB designers, assemblers, and manufacturers go through IPC standards for industry governance and quality manufacturing. By understanding and applying the correct standards in each step—design (IPC-2221), material choice (IPC-4101), fabrication (IPC-6012), assembly (IPC-A-610), and testing (IPC-TM-650)—you will enhance reliability, minimize defects, and lower costs. Besides offering uniformity and efficiency, these standards enable companies to meet global manufacturing requirements. Being up-to-date with the latest IPC revisions and applying them to design and manufacturing processes ensures ongoing success in the electronics industry.
Ensure signal integrity and minimize unwanted capacitance with Tapren's expert solutions. Let us help you enhance your design process and prevent costly setbacks. Contact us today to take your PCB performance to the next level!
Key Takeaways
IPC standards ensure the quality, consistency, and reliability of PCBs throughout the manufacturing process.
Key standards include IPC-2221 for design, IPC-4101 for materials, and IPC-A-610 for assembly, all of which are crucial for successful PCB production.
Adopting these standards helps improve performance, reduce production costs, and enhance manufacturing efficiency.
IPC standards also ensure global compliance and provide a standardized approach to PCB manufacturing across the industry.



Comments